Overview of pcb assembly services
Overview of pcb assembly services.
Pcb assembly overview:
What is the pcb assembly services?
Pcb assembly is also named (pcb smt surface mount technology)
Pcb assembly (printed circuit boards assembly),meaning that Circuit board placement is a technological process in reflow soldering. Reflow soldering, also known as reflow soldering, is a welding technology developed with the emergence of miniaturized electronic products, which is mainly used in the welding of all kinds of surface mount components. The solder of this welding technology is solder paste. Apply appropriate amount and form of solder paste on the solder pad of the circuit board in advance, and then paste the SMT components to the corresponding position; the solder paste has a certain viscosity to make the components fixed; and then let the circuit board that installs the components enter the reflow soldering equipment. The transmission system drives the circuit board through each set temperature area in the equipment, and the solder paste is dried, preheated, melted, moistened and cooled, and the components are welded to the PCB. The core link of reflow soldering is the use of external heat source heating to make the solder melt and re-flow infiltration to complete the circuit board welding process.
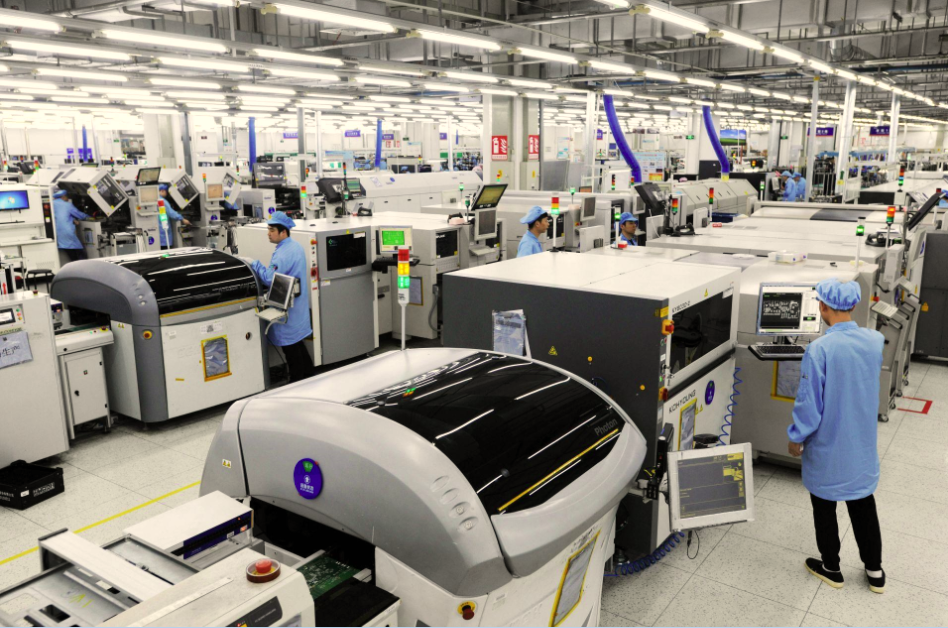

Pcb Assembly Main characteristics:
1 if the solder with strong adhesion is selected, the printing accuracy of the solder and the mounting accuracy of the components also need to be improved.
2 the external electrode of the element needs to have good wettability and wetting stability. Recommended: temperature 40 ℃, humidity 70% RH, the service life of incoming components should not exceed 6 months.
(3) the small width size of the solder zone is adopted to reduce the surface tension on the end of the element when the solder is melted. In addition, the printing thickness of solder can be reduced appropriately, such as 100 μ m.
(4) the setting of welding temperature management conditions is also a factor in the upright of components. The usual goal is to heat evenly, especially before the welding fillet of the two connected ends of the component is formed, the equalization heating should not fluctuate.
Pcb Assembly Technological process:
1. Establishment of temperature curve.
The temperature curve refers to the curve that the temperature of a certain point on the SMA changes with time when the SMA passes through the reflux furnace. The temperature curve provides an intuitive method to analyze the temperature change of a component during the whole reflow soldering process. This is very useful for achieving optimal weldability, avoiding damage to components due to overtemperature, and ensuring welding quality. The temperature curve is tested by furnace temperature tester, such as SMT-C20 furnace temperature tester.
2. Preheating section.
The purpose of this area is to heat the PCB at room temperature as soon as possible to achieve the second specific goal, but the heating rate should be controlled within an appropriate range, if too fast, there will be thermal shock, circuit boards and components may be damaged; too slow, the solvent will not volatilize enough, affecting the welding quality. Because of the fast heating speed, the temperature difference in the SMA at the back of the temperature zone is large. In order to prevent the damage of components caused by thermal shock, the maximum speed is generally stipulated to be 4 ℃ / s. However, the rising rate is usually set at 1-3 ℃ / s. The typical heating rate is 2 ℃ / s.
3. Heat preservation section.
The heat preservation section refers to the area where the temperature rises from 120 ℃ to 150 ℃ to the melting point of solder paste. Its main purpose is to stabilize the temperature of the components in the SMA and reduce the temperature difference as much as possible. Allow enough time in this area for the temperature of the larger components to catch up with the smaller components and to ensure that the flux in the solder paste is fully volatilized. By the end of the insulation section, the oxides on the pads, solder balls and component pins are removed, and the temperature of the whole circuit board is balanced. It should be noted that all components on the SMA should have the same temperature at the end of this section, otherwise entering the reflux section will cause a variety of bad welding phenomena due to the uneven temperature of each part.
4. Reflux section.
The temperature of the heater is set to the highest in this area, causing the temperature of the assembly to rise rapidly to the peak temperature. In the reflow section, the welding peak temperature varies depending on the solder paste used, and the melting point temperature of the solder paste plus 20-40 ℃ is generally recommended. For 63Sn/37Pb solder paste with melting point of 183C and Sn62/Pb36/Ag2 solder paste with melting point of 179C, the peak temperature is generally between 210C and 230C, and the reflow time should not be too long to avoid adverse effects on SMA. The ideal temperature curve is that the "tip area" that exceeds the melting point of the solder covers the smallest area.
5. Cooling section.
The lead-tin powder in the solder paste in this section has melted and fully wetted the connected surface and should be cooled as quickly as possible, which will help to get a bright solder joint and a good shape and low contact angle. Slow cooling will cause more decomposition of the circuit board into the tin, resulting in gray and rough solder joints. In extreme cases, it can cause poor tin contamination and weaken solder joint adhesion. The cooling rate of the cooling section is generally 3-10 ℃ / s, which can be cooled to 75 ℃.
6. Bridging.
Welding heating process will also produce solder collapse, this situation occurs in preheating and main heating two occasions, when the preheating temperature in the range of dozens to 100 degrees, as one of the solder components of the solvent will reduce viscosity and outflow, if the outflow trend is very strong, solder particles will be extruded outside the solder zone gold particles, in melting, if can not return to the solder zone, will also form a stranded solder ball. In addition to the above factors, whether the end electrode of the SMD element is smooth or not, whether the wiring design of the circuit board and the spacing between the solder areas are standardized, the choice of the coating method of the flux and its coating accuracy will be the reasons for the bridging.
7. Tombstone (Manhattan phenomenon).
The warping of the chip element occurs when it is subjected to rapid heating, which is because the rapid heat causes the temperature difference between the two ends of the element, and the solder on one side of the electrode gets good moisture after complete melting, while the solder on the other side is not completely melted, which leads to poor wettability. this promotes the uplift of the element. Therefore, the heating should be considered from the point of view of time elements, so that the horizontal heating to form a balanced temperature distribution to avoid the generation of rapid heat.